Regional Intravenous Anaesthesia – Bier’s block
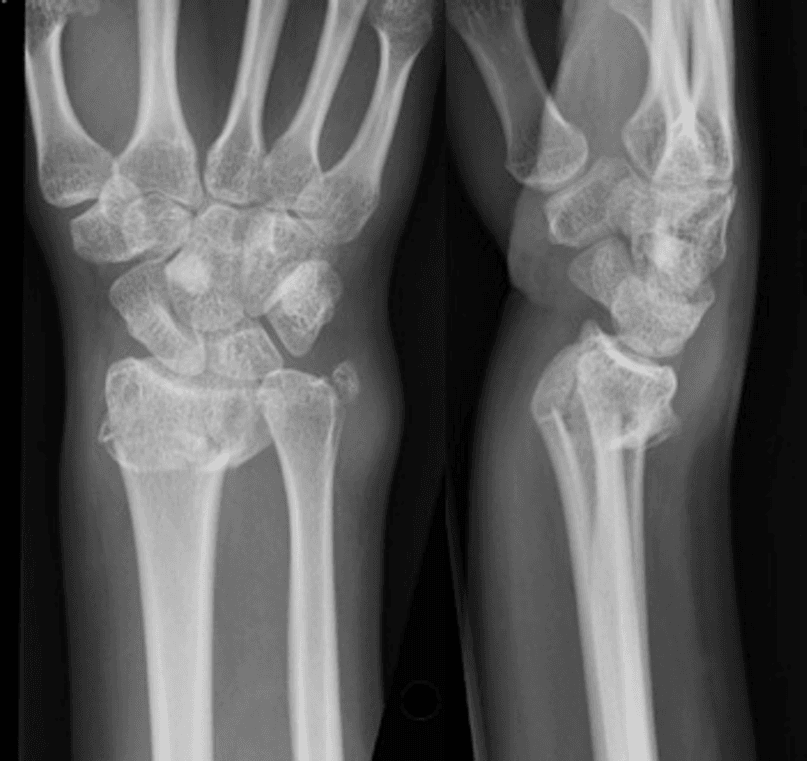
Introduction to Regional Intravenous Anaesthesia Regional intravenous anaesthesia (RIVA) is a specialised technique used to numb a limb for surgical procedures. By injecting a local anaesthetic into a vein below a tourniquet, doctors can achieve targeted pain relief without affecting the entire body. This method is particularly useful for hand and wrist surgeries, where precision […]