Introduction
Diaphragmatic hernia are problems with the diaphragm that happen at weak spots in the body’s structure. These disorders can be either congenital or acquired, with the latter typically resulting from traumatic causes. If not treated, the contents of the abdomen can push through the thoracic cavity, which needs surgery.
This aritcle is not about penetrating trauma, which is the most common cause of acquired diaphragmatic hernias. We will talk about congenital diaphragmatic hernias here because they are different and need to be addressed straight soon.
Read more surgical cases: Surgide’s Surgery Cases
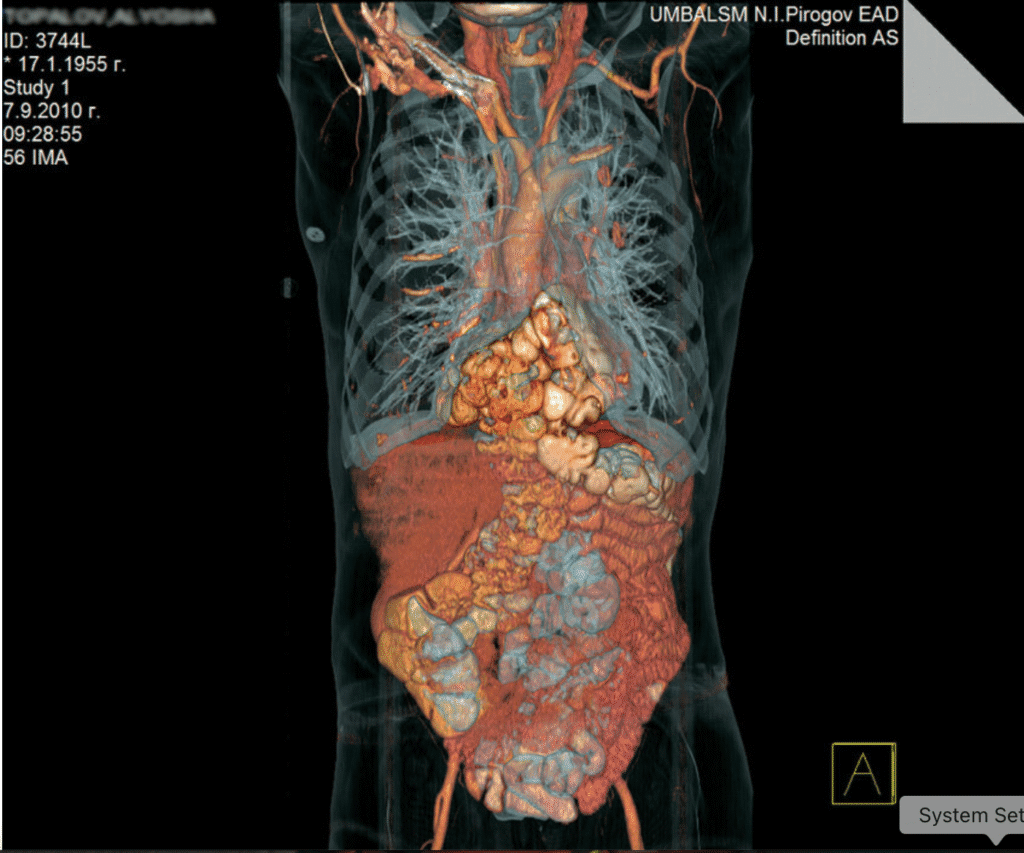
The pathophysiology of congenital diaphragmatic hernias
There are two main types of congenital diaphragmatic hernias: Bochdalek hernia and Morgagni hernia.
Bochdalek Hernia
Bochdalek hernias are the most common type, affecting roughly 1 in 5000 live births. The rear attachment of the diaphragm is to blame for these hernias. Bochdalek hernias generally happen on the left side and are often associated to other birth defects. One-third of individuals also have other congenital abnormalities.
Morgagni Hernia
Morgagni hernias are not as prevalent. but it occurs when something presses through the foramen of Morgagni, which is the space between the xiphoid process and the diaphragm’s costochondral attachments. These hernias frequently happen in the front and are more common on the right side than Bochdalek hernias. It is important to remember that this is where the diaphragm lets the internal mammary artery through and turns into the superior epigastric artery.
Clinical Presentation
Congenital diaphragmatic hernias can present with varying degrees of severity, depending on the timing and features of the hernia.
Neonates
If the hernia arises while the baby is still in the womb, it could cause pulmonary hypoplasia or problems breathing soon after birth. Neonates often have serious trouble breathing because their abdominal organs move into their thoracic cavity, which makes it harder for their lungs to expand and work.
Adults
In adults, a hernia may be asymptomatic or present with symptoms such as dyspnea (shortness of breath), atypical chest discomfort, or signs of intestinal obstruction. Bochdalek hernias in adults contain abdominal organs such as the liver, colon, or spleen in about 27% of cases.
Morgagni hernias may present clinical manifestations similar to those observed in Bochdalek hernias, including respiratory distress and abdominal pain.
Tests for Diagnosis
In babies
A straightforward erect chest radiograph (CXR) serves as the primary diagnostic tool for congenital diaphragmatic hernia in neonates. This imaging technique typically reveals bowel loops or other abdominal structures within the thoracic cavity, so confirming the hernia .
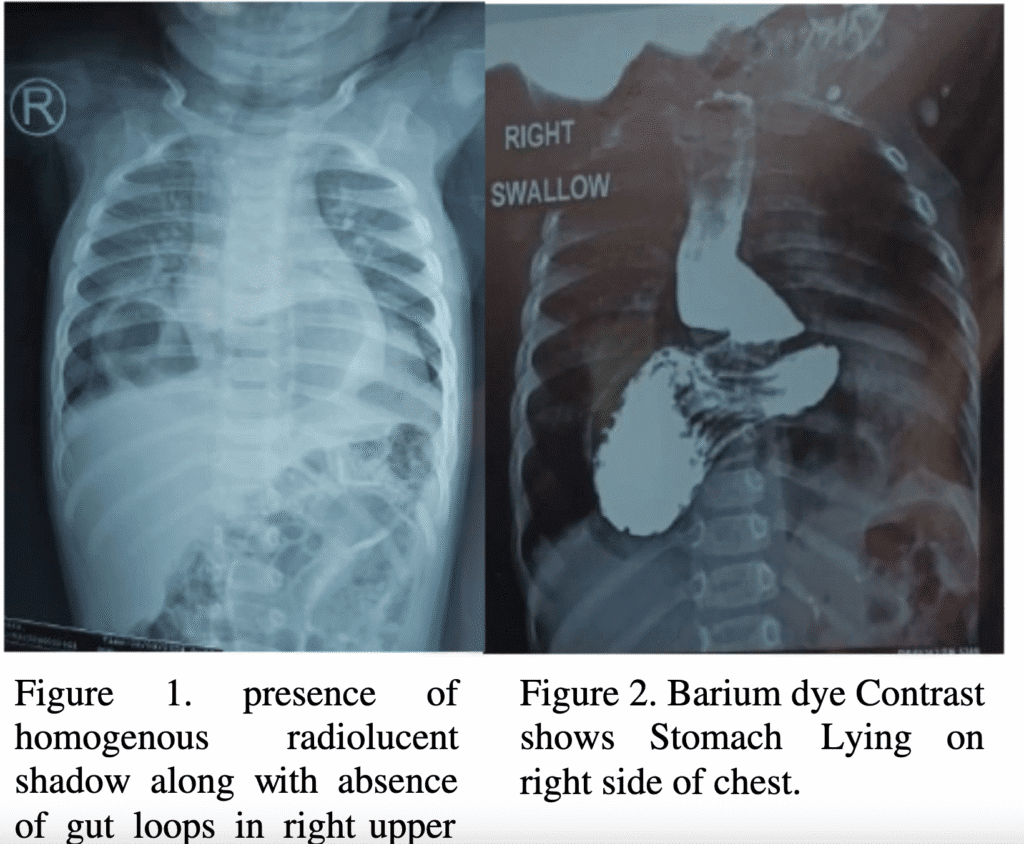
For adults
A CXR can assist clinicians figure out what’s wrong at first, but a CT scan of the chest is usually needed to obtain a better picture. A CT scan gives you more information, which helps you plan for surgery by clearly demonstrating the hernia’s size, location, and contents .
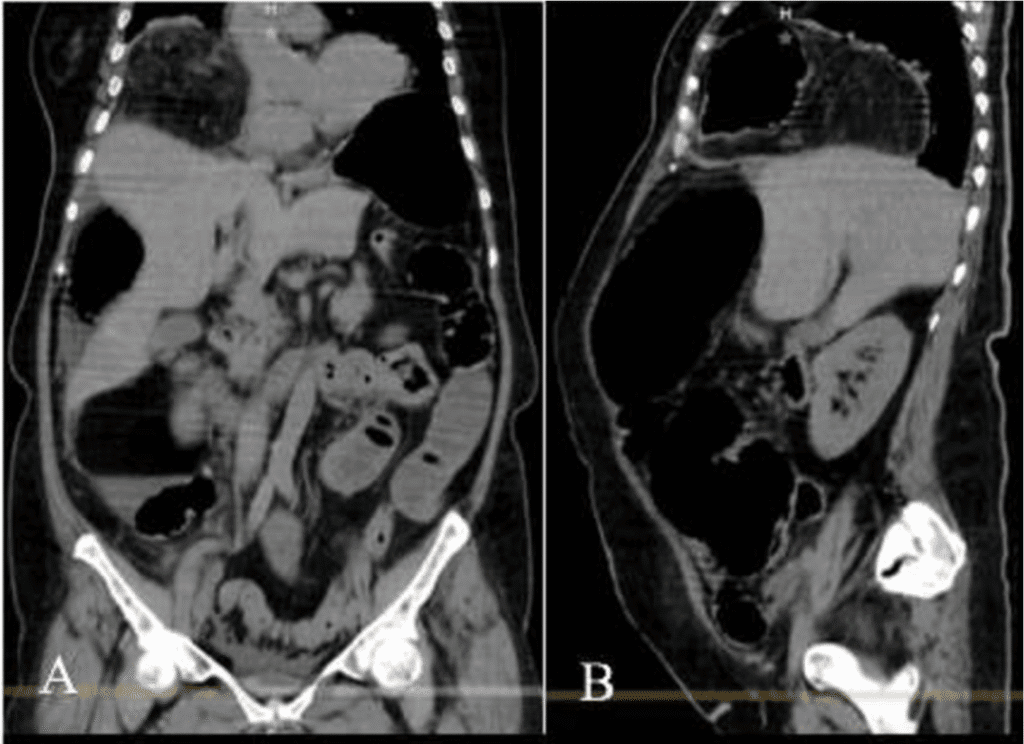
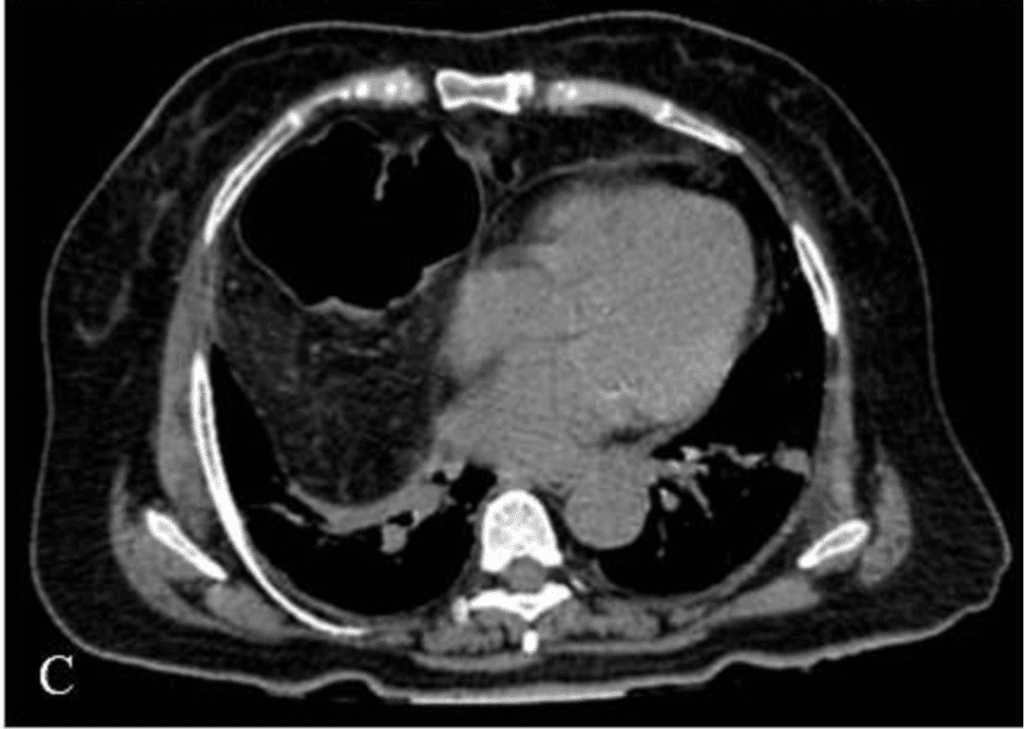
CT scan showing an anterior right diaphragmatic defect measuring 32 mm, with herniation of abdominal fat and the hepatic angle of the colon, which is compressed causing obstruction, with retrograde dilation of the ascending colon, small intestine, and gastric chamber, with free fluid in the cavity.
Surgical management
Surgical intervention is the exclusive final treatment for congenital diaphragmatic hernias. The method can be either laparoscopic or open, depending on the type and size of the hernia, the patient’s health, and the surgeon’s experience.
Things to Do Before Surgery
During surgery, the hernia is carefully pressed back into place, and any hernia sac is taken removed. After that, the opening in the diaphragm is sealed. You can seal the defect with either primary suturing or a mesh for added strength, depending on how big it is and where it is.
Things to Remember
Diaphragmatic hernias are complications that happen in the diaphragm when it is weak. They can be there at birth or come later in life.
Bochdalek and Morgagni are the two forms of congenital diaphragmatic hernias.
In neonates, congenital diaphragmatic hernias often present with significant pulmonary hypoplasia or respiratory distress, whereas in adults, they may manifest as dyspnea, chest discomfort, or signs of bowel obstruction.
Surgery, either laparoscopic or open, is the only approach to repair Bochdalek and Morgagni hernias.
Surgeons can improve the health of their patients, especially newborns, by immediately repairing congenital diaphragmatic hernias and doing surgery to fix them. This also stops issues that can emerge if hernias aren’t treated.
References:
- Dzhendov, Todor & Anzhelova, Yoana & Barguti, Fares & Kostov, Vasil & Tchervenyakov, Alexandar. (2024). Laparoscopic no-mesh repair of a large Morgagni-Larrey hernia. Bulgarian Society of Medical Sciences Journal. 6. 10.3897/bsms.6.128341.
- Cisneros-Rodríguez Gilberto, Rodríguez-Becerra Jesús M, Zecua-Mellado Yemdiel, Leon-Maldonado Emilio A, Rosales Jimenez Jose E, Alamo-Hernández Michael V, & Vazquez-Calderon Jesus A. (2025). Morgagni Hernia with Intestinal Obstruction in Adults with Diaphragmatic Plasty: Case Report. International Journal of Medical Science and Clinical Research Studies, 5(07), 1330–1335. https://doi.org/10.47191/ijmscrs/v5-i07-52
- Muhammad Tariq, Haifa Khan, Faryal Ali, Reshna Nawaz, Sadia Riaz, Morgagni Hernia in an Infant; A Case Report, Annals of PIMS
DOI: https://doi.org/10.48036/apims.v21i1.1344
